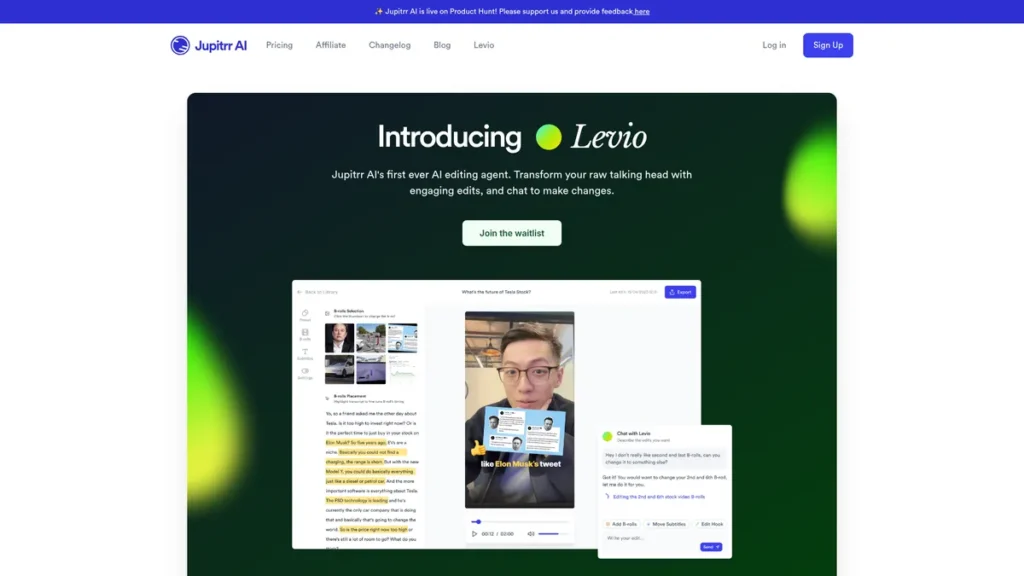
What is Levio?
Levio is an AI-driven video editing agent from Jupitrr AI, engineered to automate the post-production process for video content, particularly talking-head footage. From a technical standpoint, it functions as a processing service that ingests raw video files and applies a series of programmatic edits based on user commands. The core interaction layer is a chat-based interface, which abstracts the complexities of traditional timeline-based editors. This architecture is designed for maximum efficiency, enabling users without a background in non-linear editing (NLE) software to generate professionally styled videos by issuing natural language commands. It effectively offloads tasks like transcription, asset sourcing, and sequence timing to its AI core, aiming to significantly reduce the time and technical skill required for video production.
Key Features and How It Works
Levio’s functionality is built upon a stack of automated processes triggered through its chat interface. The workflow begins with a user uploading raw footage, which the system then analyzes to enable a command-driven editing session.
- AI-Crafted Hook: This feature performs content analysis on the initial seconds of footage to generate an engaging introductory sequence, often rearranging or highlighting key phrases to optimize for audience retention.
- Animated Subtitles: The system runs an automated speech-to-text transcription process and overlays the resulting text as dynamic, animated captions. This enhances accessibility and is crucial for silent-play environments on social media platforms.
- B-Rolls and GIFs: Based on semantic analysis of the spoken content, Levio queries integrated asset libraries (like iStock and Giphy) to retrieve and insert relevant B-roll footage and animated GIFs. This process automates what is typically a time-consuming manual search and placement task.
- Instant Changes: The chat interface serves as the primary control surface. Users issue commands like “add a zoom-in effect here” or “change the background music,” which an NLP engine parses and translates into specific editing actions on the video timeline.
- AI Background Music and Color Grading: The agent can select and apply royalty-free music tracks that match a desired mood. Similarly, it applies professional color grading presets (akin to LUTs) to standardize the video’s aesthetic.
- Emojis and Transitions: The tool provides a library of templated animations, graphical overlays (emojis), and transitions that can be inserted via simple text commands to add visual flair.
Pros and Cons
From a development and systems perspective, Levio presents a distinct set of advantages and limitations.
Pros
- High Scalability: The automated, agent-based workflow is inherently scalable. It allows content teams to increase video output volume without a linear increase in human editor headcount or software licenses.
- Reduced Technical Overhead: By abstracting complex editing functions into simple commands, Levio lowers the barrier to entry, removing the need for specialized training on platforms like Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve.
- Command-Driven Architecture: The chat interface implies a robust, command-driven backend. This structure is well-suited for future API exposure, which could allow for programmatic video generation and integration into larger content management systems.
- Operational Efficiency: The tool drastically cuts down the cycle time from raw footage to a finished product, consolidating multiple post-production steps into a single, streamlined process.
Cons
- Limited Granularity: The abstraction layer that makes it user-friendly also restricts fine-grained control. Users are limited to the set of operations and parameters the AI understands, lacking the pixel-perfect precision of a manual NLE.
- Integration Dependencies: The reliance on third-party APIs for assets like B-roll and GIFs introduces external dependencies. Any issues with these services, such as API rate limits or library changes, could impact Levio’s functionality.
- Potential for Interface Inefficiency: While simple for basic tasks, executing complex or highly specific edit sequences through a chat interface can be more cumbersome than direct manipulation on a visual timeline.
Who Should Consider Levio?
Levio is best suited for individuals and teams whose primary goal is efficient, high-volume video production over intricate artistic control.
- Content Marketing Teams: For organizations that need to produce a steady stream of social media videos, video ads, or internal training materials, Levio’s automation provides significant leverage.
- Solo Entrepreneurs and Consultants: Professionals who need to create polished video content for marketing or educational purposes but lack the time or technical expertise for traditional editing will find the platform highly effective.
- Developers and Agencies: Teams looking to prototype video content rapidly or build automated content pipelines can utilize Levio as a powerful component. Its architecture is particularly promising for those interested in programmatic content generation, should an API become available.
- Educators and Podcasters: The tool is also practical for educators creating instructional videos and for podcasters aiming to repurpose audio content into engaging visual formats for platforms like YouTube.
Pricing and Plans
At the time of this technical review, specific pricing information for Levio’s plans was not available. Service tiers in SaaS products often vary based on factors such as video output volume, resolution, length, and access to premium features like third-party asset libraries and API access. For the most accurate and up-to-date pricing, please visit the official Levio website.
What makes Levio great?
Levio’s most powerful feature is its chat-based editing interface. This design choice fundamentally reframes the video editing process, shifting it from a spatial, timeline-based paradigm to a conversational, command-driven one. From a systems perspective, this is significant because it treats video creation as a series of executable instructions parsed from natural language. This not only simplifies the user experience for non-editors but also builds a foundation for deep automation. Every edit made through the chat is a structured command, creating a workflow that is repeatable, scalable, and potentially accessible via an API for fully programmatic video synthesis in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does Levio’s AI select appropriate B-roll and music?
- Levio’s AI uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze the transcribed audio of your video. It identifies key subjects, themes, and emotional tones. Based on this semantic analysis, it queries its integrated stock media libraries (like iStock) for video clips, images, and music tracks tagged with relevant keywords, then algorithmically selects and inserts the best matches.
- What are the technical limitations on input files?
- While specific limits can change, platforms like Levio typically have constraints on the maximum file size, video duration, and supported codecs/formats for uploads. These limitations are dictated by server processing capacity and the architecture of their rendering pipeline. Users should refer to the official documentation for current specifications.
- Is there an API available for programmatic video creation?
- Currently, Levio’s primary interface is its user-facing chat application. However, the command-based nature of its architecture strongly suggests that an API could be a future offering. An API would allow developers to integrate Levio’s video generation capabilities directly into their own applications and content workflows.
- How is video rendering handled?
- Levio operates as a cloud-based service. When you finalize your edits, the rendering process is executed on their servers, not your local machine. This allows for faster processing without consuming your computer’s resources. The final video is then made available for download in standard formats, with resolution options likely tied to the user’s subscription tier.